CSS布局(中):position
position 定位方式
position:static 默认定位
默认的定位方式,元素在文档流中,无法用top,right,bottom,left进行定位
position:relative 相对定位
- 仍在文档流中
- 参照物为元素本身
- 相对定位元素层级较高
解释:
仍在文档流中:指的是,这个元素仍然会按照原来的位置占据一定的区域,下面的元素不会因此上来,右边的元素不会因此左移,比如这样:
position: static;position: relative;
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.grandparent {
margin: 10px auto 0;
height: 150px;
width: 410px;
font-family: consolas;
}
.parent {
margin: 0 auto;
height: 150px;
width: 200px;
display: inline-block;
}
.element {
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
}
.first {
background-color: gold;
}
.second {
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: white;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
}
.third {
background-color: pink;
}
.relative {
position: relative;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="grandparent">
<div class="parent">
<div class="element first"></div>
<div class="element second">position: static;</div>
<div class="element third"></div>
</div>
<div class="parent">
<div class="element first"></div>
<div class="element second relative">position: relative;</div>
<div class="element third"></div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>参照物为元素本身:也就是,元素通过
top,left等定位偏移属性,其位移的原点,是元素本来的位置。比如上面右边的,其CSS样式是这样的,向右和向下偏移了10px:.second-child{
width: 200px;
height: 50px;
background-color: lightseagreen;
position: relative;
left: 10px;
top: 10px;
color:white;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
}相对定位元素层级较高: 设置了
position的元素会比未设置的元素层级要高。可以这么理解,设置了position视作一类,没有设置的视作一类。他们分别计算层级,而前者一定高于后者。absoluterelativedefaultabsoluterelativedefault
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.element{
display: inline-block;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid white;
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
font-family: consolas;
font-size: 24px;
}
.absolute{
position: absolute;
background-color: pink;
}
.relative{
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="position: relative; z-index: 10;">
<div class="element absolute">absolute</div>
<div class="element relative">relative</div>
<div class="element default">default</div>
</div>
<div style="position: relative; z-index: 1;">
<div class="element absolute">absolute</div>
<div class="element relative" style="top: 0;">relative</div>
<div class="element default">default</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
你会发现这段代码的效果里:
- 第一行中`relative`的元素覆盖在了它后面的`default`元素上,因为`default`元素没有设置`position`
- 第一行的`relative`元素还覆盖了第二行的`relative`元素,是因为它们父元素的`z-index`值的关系。
position: absolute 绝对定位
- 脱离文档流(这个元素脱离了文档,浮出文档)
- 参照物为第一个定位祖先/根元素(也就是html元素)
- 默认宽度为内容宽度
解释:
脱离文档流:意思就是,这个元素不再占用正常文档流中的空间,且定位方法也和一般元素不一样。比如下图中:
abosolute的元素并没有占据文档的位置,而是浮在了上面,因为它脱离了文档流。具体原因会在下面讲到:defaultabsolutedefault
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
<style type="text/css">
.parent{
position: relative;
margin: 0 auto; /*为了居中*/
width: 420px;
}
.element{
display: inline-block;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 3px solid white;
background-color: lightseagreen;
color: white;
text-align: center;
line-height: 200px;
font-family: consolas;
font-size: 24px;
}
.absolute{
position: absolute;
background-color: pink;
width:120px;
height: 80px;
line-height: 80px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<div class="element default">default</div>
<div class="element absolute">absolute</div>
<div class="element default">default</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>参照物为第一个定位祖先/根元素:在相对定位元素中,我们提到,
relative元素的参照物是元素本身,而absolute元素的参照物应该是第一个已定位的祖先,如果没有这样的祖先,那么它的参照物就是根元素,也就是<html>。那么什么叫做已定位的祖先呢,就是它的已经设置了position值的祖先元素。- 第一点值得注意的是,即便对某个元素设置了
absolute,如果没有进行定位,它会保持在原来的位置上。 - 第二点值得注意的是,默认子元素会被包含在父元素的
content-box里面,但是absolute元素定位的原点,是它的第一个已定位的祖先的padding-box左上角。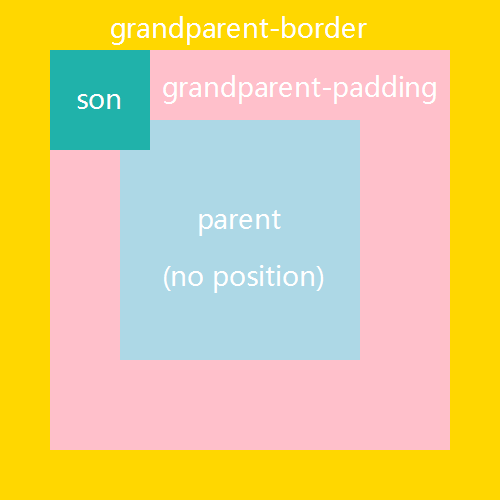
- 第一点值得注意的是,即便对某个元素设置了
默认宽度为内容宽度:即便为这个
position:absolute的元素设置成block元素,这个元素默认的宽度仍是内容的宽度。
position: fixed 固定定位
- 脱离文档流(这个元素脱离了文档,浮出文档)
- 参照物为视窗
默认宽度为内容宽度
参照物为视窗:视窗的意思就是浏览器窗口。不再多做解释。可以自己尝试一下。